In recent years, the reader will have come across concepts such as “Internet of Things” or the acronym “IoT”. A simple search in Google Trends for these concepts, as well as related concepts (“IoT systems”, “IoT systems architecture”, “IoT benefits” or “IoT employment”) shows a growing trend of interest in this concept in the last decade. But what is the Internet of Things? What is IoT? How IoT Works?
Its increasingly widespread use inside and outside the network, both in specialized and general media, relating it to sectors as different as industry, logistics, agriculture, or health, indicates the importance of the IoT and its close link with the current transformation of these sectors.
This article tries to give a global vision of IoT, being a contact with this concept and the associated technology.
What is IoT?
The concept of the Internet of Things presents a wide variety of definitions, with slight differences between them. In some cases, companies such as Cisco Systems go a step further, seeing IoT as the natural evolution of the Internet.
However, all these definitions have two ingredients as a common denominator:
- The connection between objects to the internet and its communications (communication protocols).
- The connection between things, in its broadest sense, is any physical element that generates and is capable of exchanging data for a purpose.
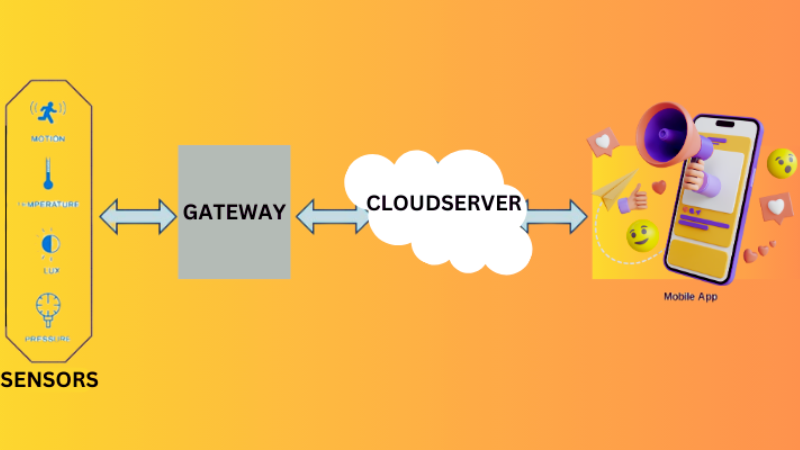
How (Internet ogThings) IoT works?
Connectivity is the cornerstone of IoT systems as it enables communication between different devices and machines, allowing the exchange of information that is so essential in the IoT.
This communication process, increasingly complex due to the evolution of the IoT, has two essential ingredients:
Identification
In order for devices to communicate with each other, they must be able to identify each other as unique entities, so there are different identifiers or identification schemes within the IoT.
Identifiers can be categorized as: object identifier, communication identifier and application identifier.
- Object identifiers represent physical or virtual objects within an IoT system. An example of this type of identifier is the barcode or RFID card.
- Communication identifiers identify nodes in a network that have communication capabilities, i.e. the ability to exchange data. The most widespread communication identifier is the IP address.
- Application identifiers identify the different service layers provided by the various applications that coexist in an IoT system, for example, the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) or the Electronic Product Code (EPC). The diverse nature of the applications providing such different services in the IoT makes such identifiers necessary.
Protocol
How the different devices in an IoT system communicate over distance can be very varied. However, by far, the most widespread is wireless communication, with protocols based on wireless technologies being the most widely used.
In terms of communication range, we must differentiate between short, medium, and long distances:
- Short distance: in this range, the most used protocol is Bluetooth, although if a faster data transmission is required, the most used is UWB (Ultra Wideband).
- Medium distance: in this range, the most widespread protocol is Wi-Fi (with its different 802.11 standards), although the ZigBee protocol, which involves the use of simpler hardware by the devices, is becoming more and more widespread.
- Long distance: in this range the most widely used is 5G, although if the required data rate is very low (areas with poor coverage) the LPWAN protocol (Low-Power Wide-Area Networking) is very widespread.
The choice of communication in IoT depends on factors like distance, frequency, data rate, power supply, hardware, and technology. A compromise is needed to select the most suitable mode for the system’s needs.
What is the IoT for?
We have talked about many concepts and characteristics of the IoT, and we can already glimpse some potential applications of this technology, but what is the Internet of Things for?
As already mentioned, the great versatility of this technology means that it can be applied and developed in very different fields. On the other hand, its intelligence quality makes it very attractive in sectors where this capability can make a difference, being an element that tips the balance in favor or against.
A wide variety of sectors are adopting this technology to simplify, improve, automate, optimize, and/or control different processes. The following are examples of some of the sectors where IoT technology has burst onto the scene:
IoT for Industry 4.0
The term Industry 4.0 was coined by the German government to describe the digitization and digital transformation of industrial systems and processes.

The simple act of deploying a low-cost sensor network for monitoring industrial processes would make it possible to predict possible failures or optimize processes after proper analysis of the collected data. This makes IoT technology very useful in any type of industry where this digital transformation is taking place.
IoT for Agriculture
Farming gets an upgrade with IoT, using sensors and drones to keep an eye on soil, crops, and pests in real-time. IoT for agriculture helps farmers make smarter decisions on watering, fertilizing, and protecting crops, leading to better yields and sustainable practices.
IoT for Health
Having an average of vital signs in real-time, as well as the history of these or the patient’s activity in certain periods, would make it possible to predict possible illnesses or ailments, developing a more active rather than reactive medicine.
IoT for health would imply a significant improvement in the treatment of patients and a more optimal use of resources.
IoT for Logistics
Real-time monitoring by means of simple RFID identifiers would boost speed and efficiency in the supply chain, avoiding unnecessary loss of time or packages.
On the other hand, the implementation of IoT systems in car fleets would imply more efficient transport management (vehicle consumption, failure prediction, driver behavior, route optimization, etc …).
IoT features
The IoT has a large number of very interesting characteristics, but of all of them, there are two in particular that give the IoT its potential for transformation when applied to sectors as different as those mentioned above. IoT features are intelligence and versatility.
To understand how these features appear in IoT systems, it is important to identify three key elements of the IoT:
- Embedded technology: includes a wide variety of devices that have sensors, input and output ports, microprocessors and memory, among many other things. Advances in device miniaturization and lower production costs have made a wide variety of low-cost embedded systems available.
- Connectivity: networks and communication protocols that allow interconnection between different devices. The development of wireless technology has facilitated the seamless connection of different devices. This rapid development enables effective communication between a wide range of devices.
- Data: all the information generated and exchanged between different devices. The correct management, storage, and analysis of the data generated in IoT infrastructures make it possible to extract value from this huge amount of data with great potential.
Thus, the emergence of cloud computing technology and the techniques and tools of big data have facilitated this aspect (IoT laboratory and Cloud development of a sensorization device).
Conclusion
In this article, you will learn what IoT is and how it works. As we can see, IoT technology has a future in a large number of sectors, and its application opens up a variety of possibilities rarely seen in other technologies.
On the other hand, the emergence of this technology is associated with the emergence of new “IoT jobs,” implying the need for workers specialized in this technology and the new IoT technologies that are yet to be developed. Thus, the need for qualified personnel and the introduction of specific training in this field is crucial.
However, the IoT, according to some experts, is not yet fully mature in some of its facets, so we have not yet glimpsed its scope, its true potential, and its needs.